[ad_1]
Struggling to harness information sprawl, CIOs throughout industries are going through robust challenges. Certainly one of them is the place to retailer all of their enterprise’s information to ship sturdy information analytics.
There have historically been two storage options for information: information warehouses and information lakes.
Information warehouses primarily retailer reworked, structured information from operational and transactional techniques, and are used for quick advanced queries throughout this historic information.
Information lakes act as a dump, storing every kind of knowledge, together with semi-structured and unstructured information. They empower superior analytics like streaming analytics for stay information processing or machine studying.
Traditionally, information warehouses have been costly to roll out since you wanted to pay for each the cupboard space and computing assets, aside from abilities to take care of them. As the price of storage has declined, information warehouses have turn out to be cheaper. Some consider information lakes (historically a extra cost-efficient various) at the moment are useless. Some argue information lakes are nonetheless fashionable. In the meantime, others are speaking a couple of new, hybrid information storage resolution — information lakehouses.
What’s the cope with every of them? Let’s take a detailed look.
This weblog explores key variations between information warehouses, information lakes, and information lakehouses, widespread tech stacks, and use instances. It additionally supplies ideas for choosing the proper resolution to your firm, although this one is difficult.
What’s an information warehouse?
Information warehouses are designed to retailer structured, curated information, organizing datasets in tables and columns. This information is definitely out there to customers for conventional enterprise intelligence, dashboards, and reporting.
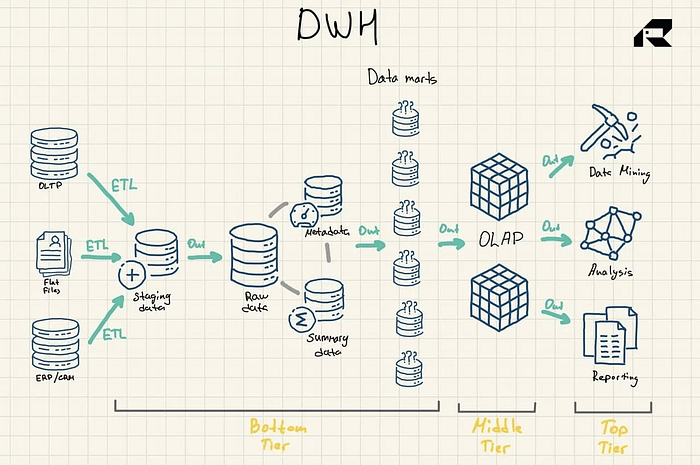
Information warehouse structure
A 3-tier structure is probably the most generally used strategy to designing information warehouses. It contains:
- Backside tier: A staging space and the database server of the info warehouse that’s used to load information from numerous sources. An extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) course of is a conventional strategy to pushing information into the info warehouse
- Center tier: A server for on-line analytical processing (OLAP) that reorganizes information right into a multidimensional format for quick calculations
- High tier: APIs and frontend instruments for working with information
Determine 1: Information Warehouse Reference Structure
There are three different important parts of an information warehouse that ought to be talked about: the info mart, the operational information storage, and metadata. Information marts belong to the underside tier. They retailer subsets of the info warehouse information, serving particular person enterprise traces.
Operational information shops act as a repository offering a snapshot of the group’s most present information for operational reporting primarily based on easy queries. They could be used as an interim layer between the info sources and the info warehouse.
There’s additionally metadata — information describing the info warehouse information — which is saved in special-purpose repositories, additionally on the backside layer.
Information warehouse evolution and applied sciences
Information warehouses have been round for a couple of many years.
Historically, information warehouses have been hosted on premises, which means firms needed to buy all {hardware} and deploy software program domestically, both paid or open-source techniques. Additionally they wanted a complete IT staff to take care of the info warehouse. On the intense facet, conventional information warehouses have been bringing in (and nonetheless achieve this as we speak) a quick time-to-insight with no latency points, whole management of knowledge along with a hundred percent privateness, and minimized safety danger.
With cloud ubiquity, many organizations now select emigrate to cloud information warehouse options the place all information is saved in a cloud. It’s analyzed in a cloud, too, utilizing some sort of an built-in question engine.
There are a selection of established cloud information warehouse options within the market. Every supplier presents its distinctive set of warehouse capabilities and completely different pricing fashions. For instance, Amazon Redshift is organized as a conventional information warehouse. Snowflake is equally. Microsoft Azure is an SQL information warehouse, whereas Google BigQuery relies on a serverless structure providing in essence software-as-a-service (SaaS), fairly than infrastructure or platform-as-a-service like, as an illustration, Amazon Redshift.
Amongst well-known on-premises information warehouse options are IBM Db2, Oracle Autonomous Database, IBM Netezza, Teradata Vantage, SAP HANA, and Exasol. They’re additionally out there on the cloud.
Cloud-based information warehouses are clearly cheaper as a result of there is no such thing as a want to purchase or roll out bodily servers. Customers pay just for the cupboard space and computing energy as wanted. Cloud options are additionally a lot simpler to scale or combine with different providers.
Serving extremely particular enterprise wants with high information high quality and quick insights, information warehouses are right here to remain for lengthy.
Information warehouse use instances
Information warehouses ship high-speed and high-performance analytics on petabytes and petabytes of historic information.
They’re essentially designed for BI-type queries. A knowledge warehouse would possibly give a solution about, as an illustration, gross sales in a specific time interval, grouped by area or division, and year-on-year actions in gross sales. Key use instances for information warehouses are:
- Transactional reporting to ship an image of enterprise efficiency
- Advert-hoc evaluation/reporting to offer solutions to standalone and “one-off” enterprise challenges
- Information mining to extract helpful information and hidden patterns from information to resolve advanced real-world issues
- Dynamic presentation via information visualization
- Drilling all the way down to undergo hierarchical dimensions of knowledge for particulars
Having structured enterprise information in a single simply accessible location exterior operational databases is just about necessary to any information mature firm.
Nonetheless, conventional information warehouses don’t help huge information expertise.
They’re additionally up to date in batch, with information from all sources processed periodically in a single go, which signifies that the info can turn out to be stale by the point it’s rolled up for analytics. The information lake appears to resolve these constraints. With a tradeoff. Let’s discover.
What’s an information lake?
Information lakes largely gather unrefined uncooked information in its authentic kind. One other key distinction between the info lake and the info warehouse is that information lakes retailer this information with out arranging it into any logical relationships which can be referred to as schemas. Nonetheless, that is how they allow extra refined analytics.
Information lakes pull in (i) transactional information from enterprise purposes equivalent to ERP, CRM, or SCM, (ii) paperwork in .csv and .txt codecs, (iii) semi-structured information equivalent to XML, JSON, and AVRO codecs, (iv) gadget logs and IoT sensors, and (v) photos, audio, binary, PDF information.
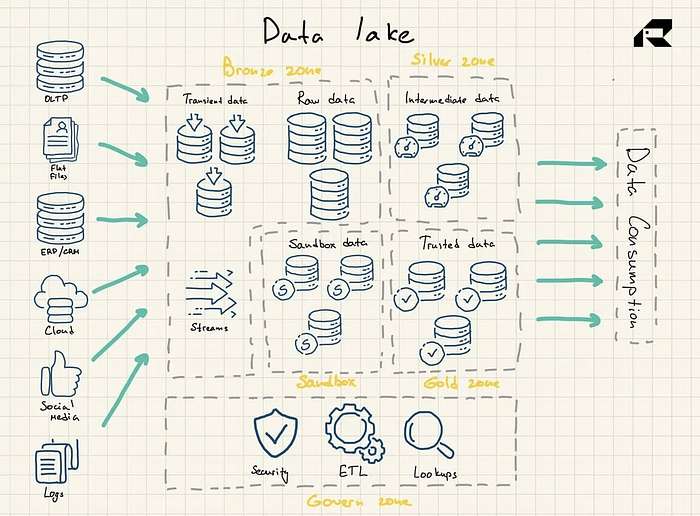
Information lake structure
Information lakes use a flat structure for information storage. Its key parts are:
- Bronze zone for all information ingested into the lake. Information is saved both as-is for batch patterns or as aggregated datasets for streaming workloads
- Silver zone the place information is filtered and enriched for exploration in keeping with enterprise wants
- Gold zone the place curated, well-structured information is saved for making use of BI instruments and ML algorithms. This zone usually options an operational information retailer that feeds conventional information warehouses and information marts
- Sandbox the place information might be experimented with for speculation validation and exams. It’s applied both as a totally separate database for Hadoop or different NoSQL applied sciences or as part of the gold zone.
Determine 2: Information Lake Reference Structure
Information lakes don’t inherently include analytics capabilities. With out them, they only retailer uncooked information that’s not helpful in its personal proper. So, organizations construct information warehouses or leverage different instruments on high of knowledge lakes to place information to make use of.
To verify an information lake doesn’t flip into an information swamp, it is very important have an environment friendly information administration technique to incorporate built-in information governance and metadata administration in information lake design. In a super world, information sitting in an information lake ought to be cataloged, listed, validated, and simply out there to information customers. That is hardly ever a case although and plenty of information lake initiatives fail. This may be averted: whatever the maturity of an information staff, it’s crucial to put in at the least important controls to implement information validation and high quality.
Information lake evolution and applied sciences
The rise of huge information within the early 2000s has introduced each grand alternatives and grand challenges for organizations. Enterprise wanted new expertise to research these huge, messy, and ridiculously fast-growing datasets to seize a enterprise impression from the massive information.
In 2008, Apache Hadoop got here up with an modern open-source expertise for gathering and processing unstructured information on an enormous scale, paving the best way for large information analytics and information lakes. Shortly after, Apache Spark emerged. It was simpler to make use of. As well as, it supplied capabilities for constructing and coaching ML fashions, querying structured information utilizing SQL, and processing real-time information.
At this time information lakes are predominately cloud-hosted repositories. All high cloud suppliers equivalent to AWS, Azure, and Google provide cloud-based information lakes with cost-effective object storage providers. Their platforms include numerous information administration providers to automate deployment. In a single state of affairs, as an illustration, an information lake would possibly encompass an information storage system just like the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) or Amazon S3 built-in with a cloud information warehouse resolution like Amazon Redshift. These parts could be decoupled from providers within the ecosystem which could embrace Amazon EMR for information processing, Amazon Glue that gives the info catalog and transformation performance, the Amazon Athena question service, or Amazon Elasticsearch Service that’s used to construct a metadata repository and index information. Native information lakes are nonetheless widespread due to common cloud issues like safety, privateness, or latency.
There are additionally on-premise storage distributors that provide some merchandise for information lakes, however their information lake choices, nonetheless, usually are not well-defined. Not like information warehouses, information lakes don’t have a few years of real-world deployments behind them. There’s nonetheless a lot criticism describing the info lake idea as blurry and ill-defined. Critics additionally argue that few folks in any group have the abilities (or enthusiasm for that matter) to run exploratory workloads towards uncooked information.
The concept that information lakes ought to be used as a central repository for all enterprises’ information must be approached with warning, they are saying. There has additionally been a provocative discuss that information lake days are numbered. The next causes are cited:
- Information lakes can’t scale compute assets effectively on demand (effectively, it is because they don’t seem to be supposed by design within the first place)
- Information lakes carry an enormous expertise debt, with their creation primarily pushed by advertising hype, fairly than technical causes (the identical has occurred with many information warehouses too)
- With the rise of cloud information warehouse options, information lakes don’t any longer provide vital price advantages (the price concern is just not that a lot simple because it’s onerous to forecast computing prices)
Such criticism is an inherent a part of any youthful expertise. Nonetheless, information lakes do have clear use instances like streaming analytics. And simply but, they don’t threaten information warehouses. Sooner or later, information lakes even triumphed over information warehouses, providing wider analytics capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and suppleness when it comes to information saved. Nonetheless, as information warehouse applied sciences have matured, many agree there is no such thing as a apparent winner now. It’s typically advisable to take care of them each or… go for a hybrid structure. Learn on.
Information lake use instances
The principle concept about information lakes is to offer enterprise entry to all out there information from all sources as rapidly as attainable. Information lakes don’t simply give an image of what occurred yesterday. Storing huge quantities of knowledge, information lakes are designed to allow organizations to study extra about each the current (utilizing streaming analytics) and the longer term (utilizing huge information options, together with predictive analytics and machine studying). Key use instances for information lakes are:
- Feeding an enterprise information warehouse with datasets
- Performing stream analytics
- Implementing ML initiatives
- Constructing superior analytics charts utilizing long-established enterprise BI instruments like Tableau or MS Energy BI
- Constructing customized information analytics options
- Operating root trigger evaluation that enables information groups to hint issues to their roots
With sturdy information engineering abilities to maneuver uncooked information into an analytics atmosphere, information lakes might be extraordinarily related. They permit groups to experiment with information to know how it may be helpful. This would possibly contain constructing fashions to dig via information and check out completely different schemas to view the info in new methods. Information lakes additionally enable wrangling with stream information that’s pouring in from internet logs and IoT sensors and isn’t suited to a conventional information warehouse strategy.
In brief, information lakes allow organizations to unearth patterns, anticipate adjustments, or discover potential enterprise alternatives round new merchandise or present processes. Used for various enterprise wants, information lakes and information warehouses are sometimes applied in tandem. Earlier than we transfer to the subsequent information storage idea, let’s rapidly recap the important thing variations between the info warehouse and the info lake.
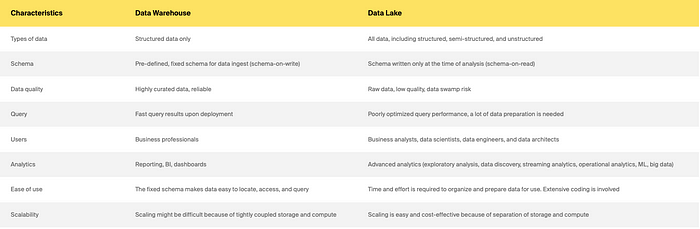
Information warehouse vs. information lake
What a couple of new hybrid structure, information lakehouses?
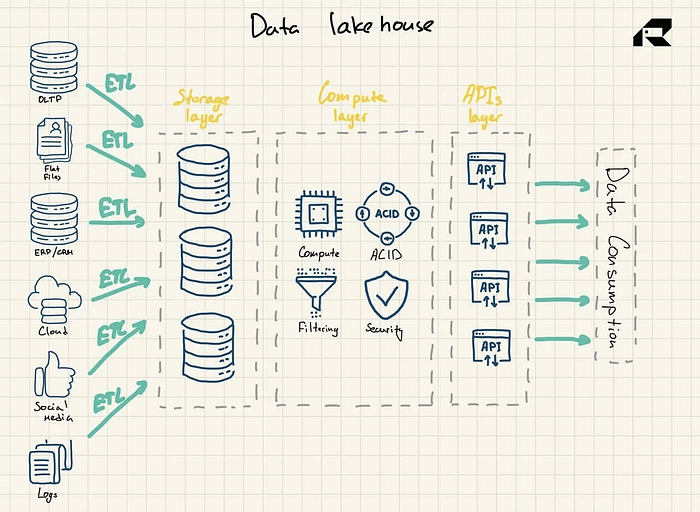
Advertising and marketing apart, the important thing concept a couple of information lakehouse is to convey computing energy to an information lake. Architecturally, the info lakehouse normally consists of:
- Storage layer to retailer information in open codecs (e.g., Parquet). This layer might be referred to as an information lake, and it’s separated from the computing layer
- Computing layer that provides the group warehouse capabilities, supporting metadata administration, indexing, schema enforcement, and ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Reliability, and Sturdiness) transactions
- APIs layer to entry information property
- Serving layer to help numerous workloads, from reporting to BI, information science, or machine studying.
Determine 3: Information Lakehouse Reference Structure
Touted as an answer marrying the perfect of each worlds, the info lakehouse addresses each:
- Information warehouse constraints, together with lack of help of superior information analytics that depends each on structured and unstructured information and vital scaling prices with conventional information warehouses that don’t separate storage from computing assets
- Information lake challenges, together with information duplication, information high quality, and the necessity to entry a number of techniques for numerous duties or implement advanced integrations with analytics instruments
The information lakehouse is a brand new development within the information analytics scene. The idea was first utilized in 2017 in relation to the Snowflake platform. In 2019, AWS used the info lakehouse time period to explain its Amazon Redshift Spectrum service that enables customers of its information warehouse service Amazon Redshift to go looking via information saved in Amazon S3. In 2020, the info lakehouse time period got here into widespread utilization, with Databricks adopting it for its Delta Lake platform.
The information lakehouse might need a vivid future forward as firms throughout industries are adopting AI to enhance service operations, provide modern services, or drive advertising success. Structured information from operational techniques delivered by information warehouses is ill-suited for good analytics, whereas information lakes are simply not designed for sturdy governance practices, safety, or ACID compliance.
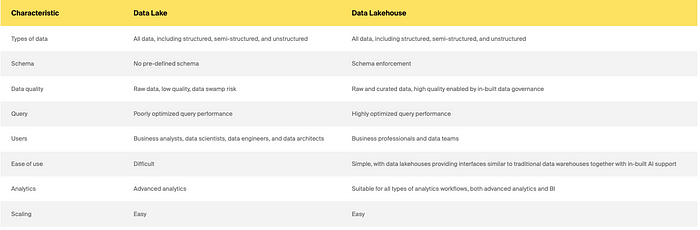
Information lake vs. information lakehouse
So information warehouse vs. information lake vs. information lakehouse: which to decide on
Whether or not you wish to construct an information storage resolution from scratch or modernize your legacy system to help ML or enhance efficiency, the precise reply gained’t be straightforward. There’s nonetheless lots of mess about key variations, advantages, and prices, with choices and pricing fashions from distributors quickly evolving. In addition to, it’s all the time a tough challenge even in case you have stakeholders’ buy-in. Nonetheless, there are some key issues when selecting the info warehouse vs. information lake vs. information lakehouse.
The first query it is best to reply is: WHY. An excellent level right here to recollect is that key variations between information warehouse, lakes, and lakehouses don’t lie in expertise. They’re about serving completely different enterprise wants. So why do you want an information storage resolution within the first place? Is it for normal reporting, enterprise intelligence, real-time analytics, information science, or different refined evaluation? Is information consistency or timeliness extra necessary for your enterprise wants? Spend a while growing use instances. Your analytics wants ought to be effectively outlined. You must deeply perceive your customers and skillsets too. A number of guidelines of thumbs are:
- A knowledge warehouse is an effective wager in case you have precise questions and know what analytics outcomes you wish to get usually.
- If you’re in a extremely regulated trade like healthcare or insurance coverage, you would possibly have to adjust to intensive reporting laws above all. So, an information warehouse will probably be a better option.
- In case your KPIs and reporting necessities might be addressed with easy historic evaluation, an information lake or a hybrid resolution will probably be an overkill. Go together with an information warehouse as a substitute.
- In case your information staff is after experimental and exploratory evaluation, select an information lake or a hybrid resolution. Nonetheless, you’ll want sturdy information analytics abilities to work with unstructured information.
- If you’re an information mature group that wishes to leverage machine studying expertise, a hybrid resolution or information lake will probably be a pure match.
Contemplate additionally your price range and time constraints. Information lakes are absolutely sooner to construct than information warehouses, and doubtless cheaper. You would possibly wish to implement your initiative incrementally and add capabilities as you scale up. If you wish to modernize your legacy information storage system, then once more, it is best to ask WHY you want this. Is it too gradual? Or doesn’t it assist you to run queries on greater information units? Is a few information lacking? Do you wish to pull out a special sort of analytics? Your group has spent some huge cash on the legacy system, so that you undoubtedly want a robust enterprise case to ditch it. Tie it to an ROI too. Information storage architectures are nonetheless maturing. It’s inconceivable to say for certain how they are going to evolve. Nonetheless, regardless of which path you’ll take, it’s helpful to acknowledge widespread pitfalls and benefit from the expertise that’s already right here.
We hope this text has cleared up some confusion about information warehouses vs. information lakes vs. information lakehouses. In the event you nonetheless have questions or want high tech abilities or recommendation to construct your information storage resolution, drop ITRex a line. They may enable you.
The put up The Definitive Information to Information Warehouse vs. Information Lake vs. Information Lakehouse appeared first on Datafloq.
[ad_2]